Conventionally, microscopes were used for better visualisation of the neural structures in the spine during decompression. The approach would be through standard midline incisions and muscle dissection.
With advances in imaging, endoscopes were used for decompression. This required tubular ports which were inserted by splitting the paraspinal muscles. The limitations however, were 2D image of the endoscope, steep learning curve and inability to use both hands (in some systems).
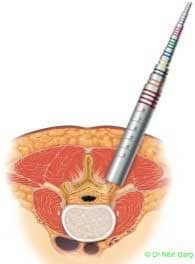
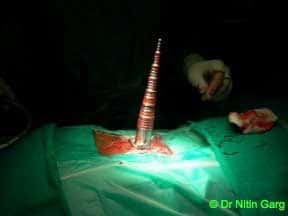
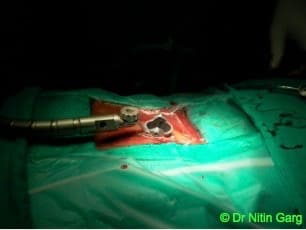
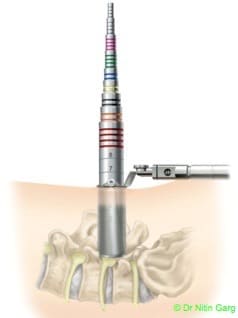
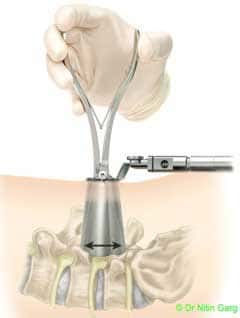
Wider and expandable ports combine the benefits of using tubular ports for accessing the region of interest in the spine and the ability to use the microscope.
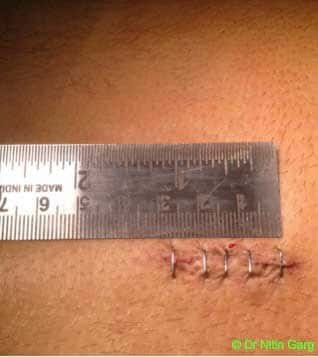
These tubular ports can be wanded (tilted) superiorly and inferiorly as also medially and laterally. This allows to access upto 2 levels of spine through the same incision. In addition, bilateral decompression of the spine can be done using one sided access.